Application
What is a CMOS-SWIR Sensor?
SWIR (Short-Wave Infrared) refers to the wavelength region of 900-2500nm. Traditional silicon sensors have an upper limit of approximately 1100nm. SWIR detection often requires camera components made of exotic materials. For example, Indium Gallium Arsenide (InGaAs) sensors (~900-1700nm range) are inherently expensive and often face challenges scaling to smaller pixel pitches and higher resolution arrays.
CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) is used in integrated circuits to to convert photons to electrons, in other terms what converts energy to create an image. A pure CMOS-based sensor is capable of SWIR wavelength detection without the use of expensive semiconductor materials, making it a cost-effective technology that enables seamless integration.

What can a SWIR camera do?
Organic Material Detection
SWIR wavelengths are absorbed and reflected according to the type of material, therefore granting the ability to view past the material into the organic matter within. This ability can be applied to agricultural technologies.


Package Component Detection
Certain plastics or objects become transparent using SWIR cameras, useful for fill detection and quality control.


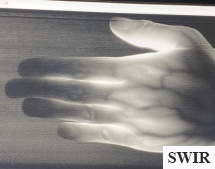
Non-invasive Blood Vein Detection
SWIR enables non-invasive bio-signal data to see beyond skin for health diagnostic or secure biometric authentication.

Packaging Inspection
Differing package materials become transparent using SWIR cameras, useful for content inspection and quality control.


Bio-Medical/Health & Biometric
Combining visual and SWIR imaging provides information on skin and tissue surfaces, offering a safer medical diagnostic, health monitoring, and secure biometric solution.



ADAS & AV
Current Advanced Driver Assistance Systems and Autonomous vehicles rely on cameras that fail to provide accurate detection of road and environmental hazards whereas it is possible with SWIR imaging.

Object detection for ADAS systems

Industrial & Machine Vision
The industrial automation and digitization of manufacturing is currently limited by the image data provided by the image sensor hardware used in machine vision systems. Implementing SWIR imaging would assist in decreasing discrepancies.
.jpg)

Improved imaging so quality control can efficiently identify any discrepancies in products.
Applications
BioMedical
With its ability to view beyond dermis layers into tissue and veins, SWIR provides useful biometric information for diagnostic and monitoring needs such as non-invasive continuous glucose monitoring.
Autonomous Vehicles
SWIR's dynamic range and inability for scattering provides much needed visual data for driver assistance systems to safely navigate in hazardous conditions as well as low-light conditions.
Consumer Products
SWIR's ability to capture longer wavelengths in low-light conditions can improve camera performance in capturing biometric data for uses like facial recognition in smartphones.
Machine Vision
Utilizing SWIR's ability to view through packaging materials as well as detecting differences in molecular structures assists industrial applications for quality control and sorting.


Download Our Non-Invasive Continuous Glucose Monitoring White Paper
Benefits
Edge Detection
Edge Detection is vital to future of machine vision and pattern recognition. Industries ranging from automotive and agriculture to distribution and warehousing can all benefit from accurate edge detection. Edge detection enables AI within vehicles to identify and differentiate the silhouette of a box or bag from that of a pedestrian crossing the street.
Additional Image Data
SWIR extends imaging capabilities beyond what is visible to the naked eye-enabling image data to be captured in any light setting.
High Resolution and Contrast
SWIR's region of the light spectrum produces images with higher resolutions when compared to NIR and MWIR imagery.
Temperature Observation
Lower SWIR wavelengths nearing the mid-wave IR (MWIR) spectrum can capture energy emitted from objects (ability to provide thermal data.)
Identification and Detection
Infrared absorbance, reflectance, and transmission can help identify and differentiate organic and inorganic materials.
Extended Visibility
SWIR sensors can detect smaller light photons making them less susceptible to scattering: penetrating through smoke, haze, or fog to produce a clearer image.